ROUTE 3. 00- 1. 01 Training » BGP Route map and MED – GNS3 Lab. In this lab we will learn how to use Route map to set MED attribute to tell which path the neighbor should choose to a specific network.
This document contains five Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) case studies. LAST UPDATE: January 27, 2016 Performance Routing v3 (PfRv3) is the Cisco next generation Intelligent Path Control. This guide is based on IOS 15.6(1)T with. Error opening tftp (Timed out)
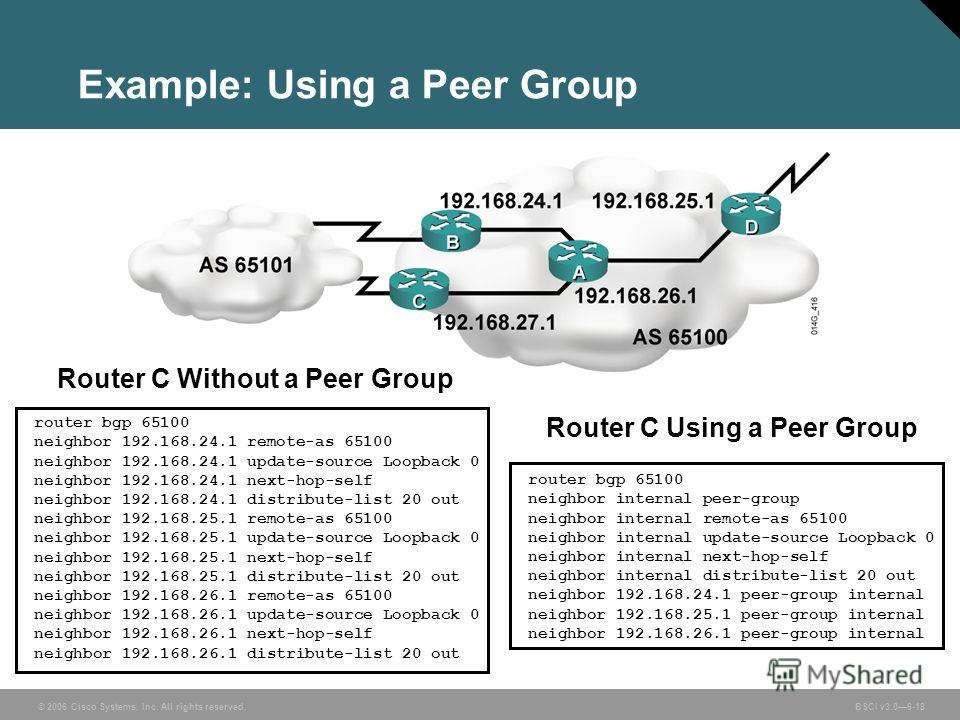
R1: router bgp 123 neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 123 neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source loopback0 neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 123 neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source loopback0. In this post, let me get some summary of Cisco BGP timers that you can find useful in real life as they reflect basic convergence and route propagation throughout a BGP v2.01 – Aaron Balchunas * * * All original material copyright © 2007 by Aaron Balchunas ( aaron@routeralley.com), unless otherwise noted. Chapter Description This chapter from Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Foundation Learning Guide: (CCNP ROUTE 300-101) examines the Open Shortest Path First.
Topology: IOS used in this lab: c. Tasks in this lab: 1) Set up basic IBGP & EBGP2) Advertise loopback 1 & loopback 1. R1 3) Use route- maps on R2 & R3 to set MED for only 1. R6 and will R6 see network 1. Basic Configuration – IP Assignments. Download Tmpgenc Authoring Works 4 Full Crack there. R1: interface f. 0/0ip address 1. R4: interface f. 1/0ip address 4.
R2: interface f. 0/0ip address 1. R5: interface f. 1/0ip address 5.
R3: interface f. 0/0ip address 1. R6: interface f. 0/0ip address 4. Set up IBGP & EBGP connections. R1: router bgp 1. Note: R1 establishes BGP neighbor relationships with R2 & R3 via their loopback interfaces but R1does not know how to reach there (and neighbor relationship can not be established) so the most simple way is to use a static route. R4: router bgp 4.
Note: the “next- hop- self” feature is used so that networks learned from R2 will beadvertised to R6 with R5’s next- hop IP address. If notthe networks learned from R2 would be markedas “inaccessible” on R6 (because R4 would advertise with. R2’s IP address but R6 can not reach the next- hop 2.
R2: router bgp 1. R5: router bgp 4. R3: router bgp 1.
R6: router bgp 4. Note: The use of a loopback interface to define neighbors is common with i. BGP, but is not common with e. BGP. Normally, you use the loopback interface to make sure that the IP address of the neighbor stays up and is independent of hardware that functions properly. In the case of e. BGP, peer routers frequently have direct connection, and loopback does not apply. Advertise networks 1.
R1: On R1 we advertise two networks 1. R1: router bgp 1.
In fact we don’t need the “mask 2. C IP address. Now check on both R2 & R3 to see both networks are advertised. Also on EBGP neighbors, these networks are also advertised (you have to wait a moment for BGP updates)On R6 networks 1.
R4 & R5: Note: the path via R4 (4. ID on R4)3) Use route- maps on R2 & R3 to set MED for 1.
R2: router bgp 1. MED. The metric advertised by R3 is lower so it is chosen as the best path to 1. Notice that updates for 1.